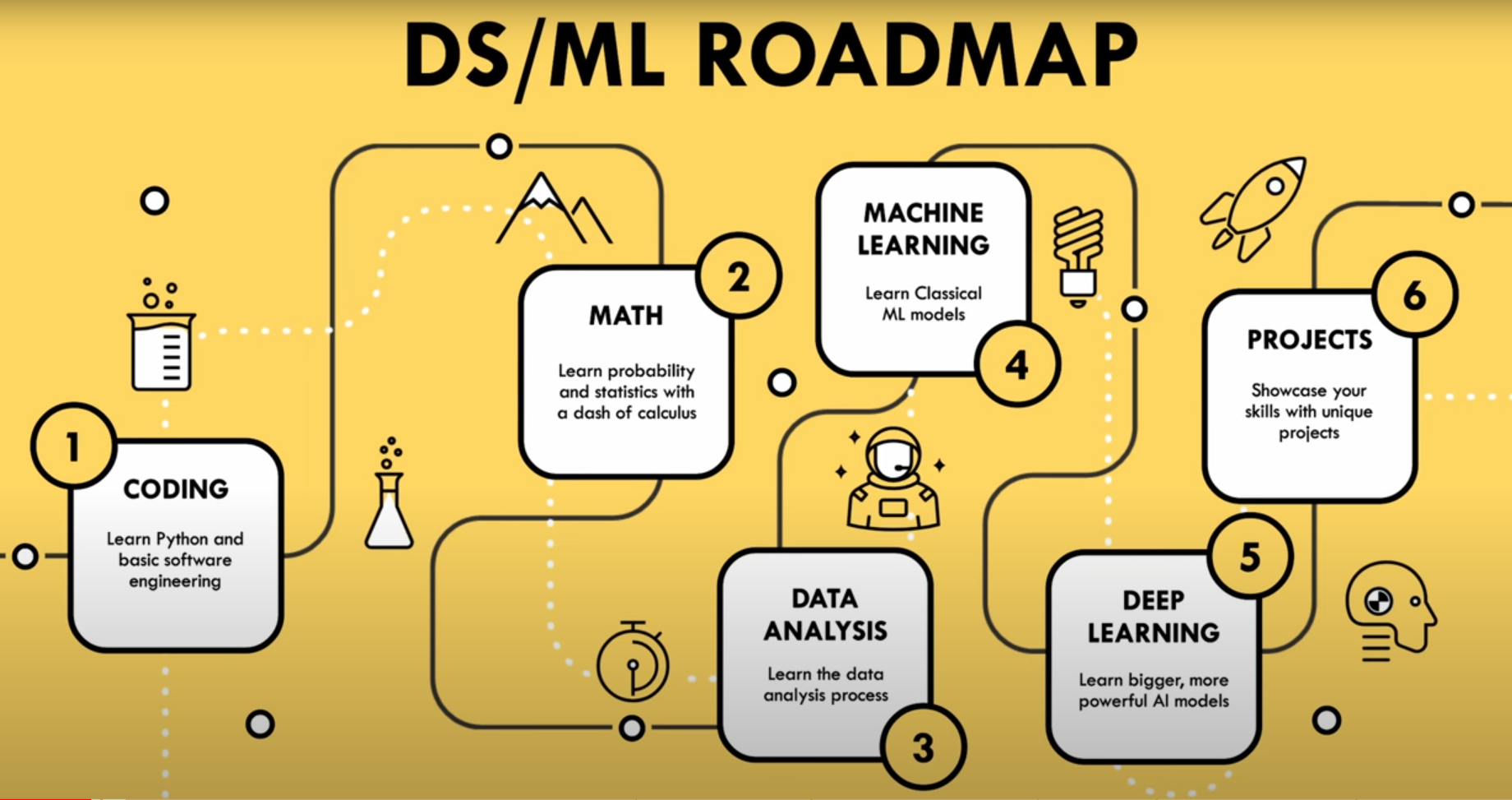
Becoming a Data Scientist in 2024: Roadmap
Published:
As the data landscape continues to evolve in 2024, becoming a data scientist requires a multi-faceted approach, encompassing coding, mathematical proficiency, data analysis, and machine learning. This guide outlines a comprehensive roadmap to becoming a proficient data scientist, integrating essential skills and modern practices such as working with Large Language Models (LLMs) and prompt engineering.
From my perspective, transitioning into data science feels both challenging and exhilarating. My background in data analytics and a Ph.D. in bioinformatics has given me a solid foundation in mathematics and deep learning. My experience in physics has honed my analytical skills, but my journey into data science requires a shift towards mastering programming and building a visible portfolio. This blog marks the beginning of my transition and aims to serve as a guide for anyone on a similar path.
1. Mastering Coding: The Foundation of Data Science
Coding is the bedrock of data science, and Python is the language of choice due to its versatility and extensive libraries tailored for data analysis and machine learning. Here’s how to start:
- Python Programming for Beginners by Mosh Hamedani: This tutorial offers a thorough introduction to Python, covering basic syntax, data structures, and includes hands-on projects to cement your understanding.
2. Strengthening Math Skills
While data science tools handle complex math, a solid grasp of fundamental mathematical concepts is crucial. Focus on the following areas:
Probability and Statistics by Khan Academy: This course offers a detailed overview of probability and statistics, crucial for understanding data distributions and model evaluations.

3. Data Analysis & SQL: The Core Skills
Data analysis involves collecting, cleaning, and interpreting data. Proficiency in SQL and data analysis libraries is essential:
Introduction to Data Analysis by Udacity: Learn SQL to manage and analyze relational databases, a fundamental skill for data querying and manipulation.
Python Libraries for Data Analysis:
- NumPy: For numerical computing.
- Pandas: For data manipulation and analysis.
- Matplotlib: For data visualization.
4. Exploring Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a pivotal area in data science, involving algorithms that enable computers to learn from data:
Machine Learning Specialization by DeepLearning.AI: This specialization covers supervised and unsupervised learning, and includes practical projects for experience.

5. Diving into Deep Learning
Deep learning, a subset of ML, employs neural networks to model complex patterns in data. Focus areas include:
Deep Learning Specialization by DeepLearning.AI: This course covers advanced topics like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for image data and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) for sequential data.

6. Working with Large Language Models (LLMs) and Prompt Engineering
In 2024, familiarity with LLMs like GPT and understanding prompt engineering is invaluable for tasks involving text generation and natural language understanding:
Introduction to Large Language Models: This guide provides an overview of how LLMs work and their applications.

Prompt Engineering for AI: This course by Deeplearning.AI explores the techniques of crafting effective prompts to leverage the power of LLMs for various applications.

7. Building Real-World Projects
Application of skills through projects is critical for reinforcing learning and showcasing your expertise:
Kaggle Competitions: Participate in data science competitions to solve real-world problems and gain practical experience.

Data Science Portfolio Projects by Towards Data Science: Explore examples of impactful data science projects to inspire and guide your own work.
Final Thoughts
Becoming a data scientist in 2024 involves a blend of foundational skills and modern techniques. Embrace continuous learning, from mastering Python to exploring the depths of machine learning and LLMs. Remember, practical experience through projects is invaluable for solidifying your knowledge and demonstrating your capabilities.
Stay curious, keep experimenting, and join the thriving community of data scientists driving innovation in the age of data.
References: